Temperature Sensor LM35 in Arduino with C#
Temperature sensor LM35 in Arduino with CSharp
1. Problem Statement
In this tutorial we will learn how use temperature sensor LM35 to get
temperature from the environment in Arduino and process the information
in C# via the serial Port, Also we will show the temperature in Celsius
and Fahrenheit degrees.
2. LM35 Precision Centigrade Temperature Sensors
The LM35 is integrated-circuit temperature sensor, whose output voltage
is linearly proportional to the Celsius (Centigrade) temperature. The
LM35 thus has an advantage over linear temperature sensors calibrated in
° Kelvin, as the user is not required to subtract a large constant
voltage from its output to obtain convenient Centigrade scaling. The
LM35 does not require any external calibration or trimming to provide
typical accuracies of ±1⁄4°C at room temperature and ±3⁄4°C over a full
−55 to +150°C temperature range. Low cost is assured by trimming and
calibration at the wafer level.. The LM35 is rated to operate over a
−55° to +150°C temperature range.
Previously we need to understand couple of things, so to connect it to
Arduino, you must connect VCC to Arduino 5V, GND to Arduino GND, and the
middle pin you must connect to an Analog Pin, in my case we will use
A0(Analog pin).
This projects doesn't need any resistor or capacitor between the Arduino
and the Sensor, but you need to know that Arduino ADC has a precision
of 10 bits. This means:
5V / 2^10 = 5V / 1024, so 0.0049 is our factor. To get the temperature in Celsius from LM35, we calculate like this:
Temperature Celsius = (pinA0 * 0.0049)*100
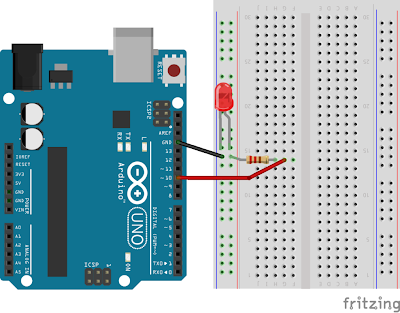
3. Sketch for this project
For implement this project we will required the following materials:
- LM35 temperature sensor
- Couple of Wires
- Arduino UNO R3
The next picture show the sketch for this project

4. Source code to Get Temperature from LM35 in Arduino
Go to Arduino text Area and type de following code, first we define the
analog Pin, sensorValue and temperature in Celsius, second we start to
open communication for serial, third we get the voltage from LM35 and
convert to celsius degree and write in the serial port and get the
information from C# and show the temperature.
#define sensorPin 0 //A0 Pin
int sensorValue = 0;
float celsius = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); //start Serial Port
}
void loop() {
getTemperature();
//send celsious value to Port and read from C#
Serial.println(celsius);
delay(1000);
}
void getTemperature(){
//get sensorPin voltage
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
//convert voltage to celsius degree
celsius = (sensorValue * 0.0049) *100;
}
5. Design Project in C# to show temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit
Design an interface like depicted in next figure, for design the
thermometer I used the Old GDI+, also we will add a TextBox to show the
temperature get from serial Port and finally one Button to show the
temperature in the thermometer.

The next code is for button Show temperature, first we verify if the
port is open and after get the temperature from serial port which was
send by arduino and round this value and send that value to a function
which is in charge to draw the current temperature in the thermometer.
private void btnShowTemperature_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (serialPort1.IsOpen)
{
//get Temperature from serial port sent by Arduino
int temperature = (int)(Math.Round(Convert.ToDecimal(
serialPort1.ReadLine()), 0));
txtTemperature.Text = temperature.ToString();
//draw temperature in the thermometer
DrawTemperatureLevel(temperature);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
}
6. Running the project
First in arduino UNO R3 press the button Upload and then go to visual
studio and run the project, second press the button Show Temperature and
then it will show the temperature in the thermometer as shown next
figure.